Health Monitoring¶
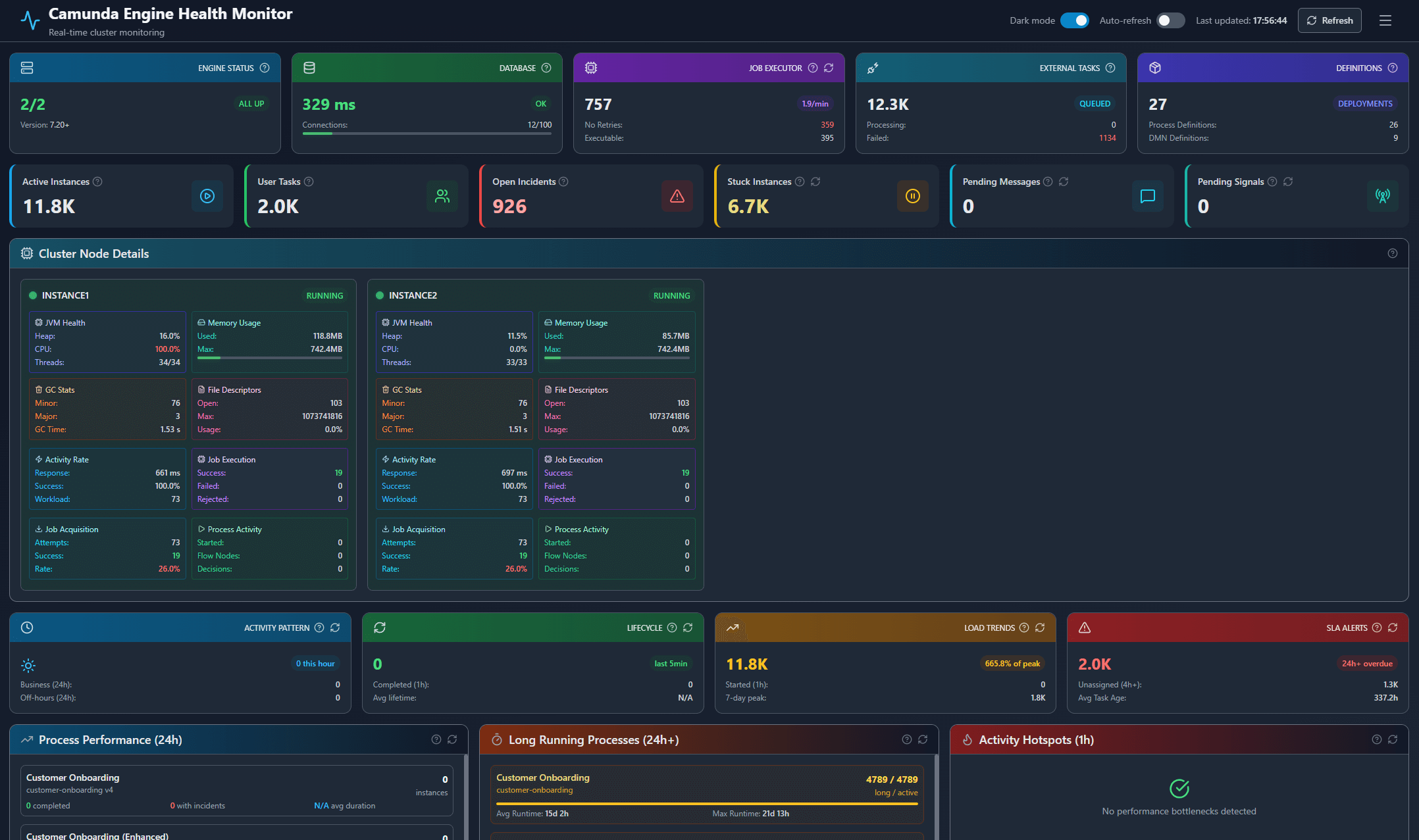 Real-time cluster health overview with JVM metrics and performance insights
Real-time cluster health overview with JVM metrics and performance insights
Overview¶
The Health Monitoring dashboard provides comprehensive, real-time visibility into your Camunda 7 cluster's health and performance. It consolidates metrics from all cluster nodes, JVM telemetry, database health, and operational insights into a single, unified interface designed for DevOps, SRE, and operations teams.
Key Capabilities¶
🎯 Cluster-Wide Visibility¶
Monitor the status and performance of all Camunda nodes in your cluster simultaneously:
- Node Status Tracking - Real-time status indicators (RUNNING, DOWN, ERROR) for each configured node
- Response Time Monitoring - Track API response latency for each node to identify performance bottlenecks
- Workload Distribution - Visualize workload scores across nodes to detect load imbalances
- Job Executor Health - Monitor job acquisition rates, execution success rates, and rejection patterns
🔍 Deep JVM Insights¶
Get detailed visibility into the Java Virtual Machine performance for each node:
- Memory Management - Real-time heap usage, utilization percentages, and memory pressure indicators
- Garbage Collection - Track minor and major GC events, total GC time, and potential memory issues
- Thread Monitoring - Current, peak, and daemon thread counts to identify thread exhaustion
- CPU & System Load - Process CPU load, system load averages, and overall resource utilization
- File Descriptors - Monitor open file descriptors to prevent resource exhaustion
The dashboard automatically detects whether your nodes expose JVM metrics via JMX exporters or Micrometer (Quarkus) and adapts accordingly.
💾 Database Health¶
Monitor the PostgreSQL database that powers your Camunda cluster:
- Connection Health - Database latency measurements via simple query probes
- Connection Pool Monitoring - Active vs. max connections with utilization percentages
- Storage Analysis - Identify the largest Camunda tables for capacity planning
- Archival Opportunities - Count completed process instances eligible for archival (90+ days old)
- Slow Query Detection - Identify long-running queries impacting performance (requires
pg_stat_statementsextension)
📊 Process Analytics¶
Gain operational insights into your process execution patterns:
- Process Performance - View total instances, completion rates, failure rates, and average durations for each process definition
- Activity Hotspots - Identify slow or frequently-executed activities that may need optimization
- Error Patterns - Analyze incident types, frequencies, and affected processes to prioritize fixes
- Long-Running Instances - Track processes running longer than expected with runtime breakdowns
⚡ Real-Time Metrics¶
Stay informed about current system activity and throughput:
- Business Hours Activity - Compare instance starts during business hours vs. off-hours
- Completion Rates - Track instances completed in the last hour
- Average Lifetime - Monitor typical process execution times
- Throughput Trends - Compare current load against peak activity over the last 7 days
🚨 SLA & Resource Alerts¶
Proactively identify issues before they impact operations:
- Overdue Tasks - Identify user tasks overdue by 24h, 72h, or more
- Unassigned Tasks - Track tasks without assignees that are aging
- Dead Letter Jobs - Monitor jobs that have exhausted all retries
- Resource Usage - Track total variables, blob variables, and execution counts
📈 System Health Indicators¶
Understand your system's operational status:
- Deployment Activity - Recent deployments (24h, 7 days) and total deployment count
- Core Metrics - Active instances, user tasks, external tasks, and incidents at a glance
- Job Executor Stats - Total jobs, failed jobs, active timer jobs, and external task states
- Definitions - Count of deployed process definitions and DMN decision tables
Features in Detail¶
Auto-Refresh Mode¶
Enable continuous monitoring with configurable auto-refresh:
- Automatically refreshes light metrics every 30 seconds
- Keeps dashboard current without manual intervention
- Toggle on/off with a single click
Dark Mode Support¶
Switch between light and dark themes for comfortable viewing in any environment. Your preference is automatically saved.
Lazy Loading Architecture¶
The dashboard uses intelligent lazy loading to minimize initial load time:
- Initial Load - Displays essential metrics immediately (cluster status, database health, core counts)
- On-Demand Loading - Heavy analytics sections load only when viewed
- Progressive Enhancement - Each section loads independently without blocking others
- Smart Caching - Already-loaded sections refresh efficiently
Responsive Design¶
The dashboard adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes, from desktop monitors to tablets.
Prometheus Integration¶
For teams using enterprise monitoring stacks, Champa Intelligence exposes all metrics via native Prometheus endpoints.
Available Endpoints¶
Light Metrics Endpoint
- Purpose: Essential, low-overhead metrics for real-time alerting - Recommended Scrape Interval: 15-30 seconds - Includes: Node status, JVM heap, DB latency, active instances, incidentsFull Metrics Endpoint
- Purpose: Comprehensive metrics for detailed dashboarding and historical analysis - Recommended Scrape Interval: 5 minutes - Includes: All light metrics plus detailed job executor stats, per-process KPIs, database table sizes, slow queries, and moreExample Grafana Queries¶
Monitor your cluster with powerful PromQL queries:
# Average heap utilization across all nodes
avg(camunda_jvm_heap_utilization_percent)
# Alert when a node goes down
camunda_node_status == 0
# Top 5 processes by incident count
topk(5, camunda_process_open_incidents)
# Database connection pool usage alert
camunda_db_connection_utilization_percent > 80
# Job success rate per node
camunda_node_job_success_rate < 95
Integration Benefits¶
- Unified Monitoring - Correlate Camunda health with other system metrics
- Custom Dashboards - Build tailored views in Grafana or your preferred tool
- Historical Trending - Analyze performance patterns over time
- Alert Management - Set up sophisticated alerting rules based on any metric
Using the Dashboard¶
Initial View¶
When you first access the dashboard, you'll see:
- Cluster Status Panel - Overview of running vs. total nodes with version info
- Database Status Panel - Connection health, latency, and pool utilization
- Job Executor Panel - Current job counts and execution states
- External Tasks Panel - Active external tasks and retry status
- Definitions Panel - Deployed process and decision definitions
- Core Metrics Panel - Active instances, user tasks, and incidents
Node Details¶
Expand any node card to view:
- JVM health metrics (heap, CPU, threads, GC stats)
- Memory usage with visual indicators
- File descriptor utilization
- Activity rates and workload scores
- Job acquisition and execution statistics
- Process activity breakdown
Color-coded indicators help you quickly identify:
- 🟢 Green: Healthy, normal operation
- 🟡 Yellow: Warning thresholds exceeded
- 🔴 Red: Critical issues requiring attention
Analytics Sections¶
Click on any collapsible section to load detailed analytics:
- Process Analytics - Performance breakdown per process definition
- Activity Hotspots - Slow or high-volume activities
- Error Patterns - Incident analysis and troubleshooting insights
- Long Running Instances - Processes exceeding expected durations
- Dead Letter Jobs - Failed jobs requiring intervention
- Database Storage - Table sizes and archival candidates
- Slow Queries - Database performance bottlenecks
Each section loads independently and caches results for fast subsequent access.
Technical Architecture¶
The Health Monitoring system is built on a parallel data collection architecture for maximum performance:
- Concurrent Node Polling - All cluster nodes are queried simultaneously using thread pools
- JMX/Micrometer Integration - Automatic detection and parsing of JVM metrics from either source
- Intelligent Caching - Reduces database load through smart query optimization
- RESTful API Design - Each metric group has a dedicated endpoint for granular loading
- Prometheus-Native - First-class support for Prometheus scraping and PromQL
Configuration¶
The system is configured via environment variables and config files:
CAMUNDA_NODES- Dictionary of node names and REST API URLsJMX_EXPORTER_ENDPOINTS- JMX exporter URLs per nodeJVM_METRICS_SOURCE- Set to 'jmx' or 'micrometer' based on your setupSTUCK_INSTANCE_DAYS- Threshold for considering instances "stuck" (default: 7)
Best Practices¶
Monitoring Strategy¶
- Set Up Baseline Metrics - Understand your normal operating parameters
- Enable Auto-Refresh - Keep the dashboard open during critical operations
- Configure Alerting - Use Prometheus endpoints to trigger alerts for critical conditions
- Review Regularly - Check activity hotspots and error patterns weekly
- Plan Capacity - Use database storage metrics to plan archival and scaling
Performance Tips¶
- Use the light metrics endpoint for high-frequency Prometheus scraping
- Enable lazy loading (default) to minimize initial dashboard load
- Consider database archival when completed instances exceed 90 days old
- Monitor heap utilization and plan JVM tuning before reaching 80%
- Track slow queries and add indexes where beneficial
Troubleshooting¶
Node shows ERROR status
- Verify the node is reachable via the configured REST API URL
- Check authentication credentials (CAMUNDA_API_USER, CAMUNDA_API_PASSWORD)
- Review node logs for startup issues
JVM metrics show NO_JMX_DATA
- Confirm JMX exporter or Micrometer is properly configured on the node
- Verify JMX_EXPORTER_ENDPOINTS contains the correct URL
- Check JVM_METRICS_SOURCE matches your setup (jmx vs. micrometer)
Database latency is high
- Review slow queries if pg_stat_statements is enabled
- Check database connection pool size vs. active connections
- Consider optimizing or indexing identified slow queries
API Reference¶
REST Endpoints¶
| Endpoint | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
/health | GET | Main dashboard page |
/health/api/full | GET | Complete health data (JSON) |
/health/api/metrics/<group> | GET | Specific metric group (lazy load) |
/health/api/individual/<metric> | GET | Single metric value |
/health/api/block/<block> | GET | Individual analytics block |
/health/light/metrics | GET | Prometheus metrics (light) |
/health/full/metrics | GET | Prometheus metrics (full) |
Metric Groups¶
process-analytics- Process definitions, completions, failuressystem-health- Deployments, dead letter jobs, long-running instancesquick-metrics- Business hours activity, lifecycle metricssla-metrics- Overdue tasks, resource alertsthroughput-metrics- Load trends, peak comparisonsjmx-metrics- JVM health for all nodesdatabase-metrics- Table sizes, slow queries, archival data
Individual Metrics¶
stuck-instances- Count of processes stuck beyond thresholdjob-throughput- Jobs executed per minutepending-messages- Message event subscriptions waitingpending-signals- Signal event subscriptions waiting
FAQ¶
Q: How often should I refresh the dashboard?
A: The light metrics refresh every 30 seconds in auto-refresh mode, which is suitable for most monitoring scenarios. For Prometheus scraping, use 15-30 seconds for light metrics and 5 minutes for full metrics.
Q: Can I monitor multiple clusters?
A: Currently, each Champa Intelligence instance monitors one Camunda cluster. Configure CAMUNDA_NODES with all nodes in your target cluster.
Q: What if my nodes don't expose JMX metrics?
A: The dashboard will function without JVM metrics, showing node status and Camunda-specific metrics. JVM insights simply won't be available for those nodes.
Q: How do I enable pg_stat_statements for slow query detection?
A: Add shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_stat_statements' to your PostgreSQL configuration and restart. Then run CREATE EXTENSION pg_stat_statements; in your database.
Q: Can I export the dashboard data?
A: Yes, use the /health/api/full endpoint to retrieve all metrics as JSON, or scrape the Prometheus endpoints for time-series data.