Model Validator (Linter)¶
 Automated quality checks for BPMN and DMN models with customizable rules
Automated quality checks for BPMN and DMN models with customizable rules
Overview¶
The Model Validator (Linter) is an automated quality assurance tool that analyzes BPMN and DMN models against best practices, organizational standards, and potential issues before deployment. Think of it as a spell-checker and style guide for your process models—catching mistakes, enforcing conventions, and identifying security risks early in development.
With over 70 pre-configured rules covering everything from basic syntax to advanced security patterns, the linter helps teams maintain consistent, high-quality process models across the organization.
Why Use Model Validation?¶
Problems It Solves¶
Without validation:
- ❌ Models deploy with configuration errors that cause runtime failures
- ❌ Each developer follows different naming and documentation conventions
- ❌ Security vulnerabilities (hardcoded credentials, SQL injection) go undetected
- ❌ Performance issues (blocking code, missing async configuration) discovered in production
- ❌ Hours spent debugging issues that could have been caught in seconds
With validation:
- ✅ Catch configuration errors before deployment
- ✅ Enforce consistent standards across all models
- ✅ Identify security risks automatically
- ✅ Prevent performance anti-patterns
- ✅ Accelerate code reviews with automated checks
Key Capabilities¶
🎯 Dual Model Support¶
BPMN Validation
- Process structure and flow validation
- Camunda-specific configuration checks
- Script syntax and API usage validation
- Service task and user task configuration
- Call activity, timer, and event validation
DMN Validation
- Decision table structure validation
- Input/output configuration checks
- Literal expression complexity analysis
- Decision dependency validation
- Camunda DMN-specific settings
📋 70+ Validation Rules¶
The validator includes a comprehensive rule set organized into categories:
1. Best Practice Enforcement (15 rules)
- Element naming conventions
- Documentation requirements
- Executable process flags
- Gateway flow naming
- Subprocess structure validation
2. Camunda-Specific Validation (25 rules)
- Service task implementation (class, delegate, expression, external topic)
- User task assignment (assignee, candidate users/groups)
- Timer event definitions (duration, date, cycle)
- External task topics
- Call activity bindings
- Multi-instance configuration
- Form field validation
- I/O mapping validation
- Async continuation and retry configuration
3. Script Intelligence (15 rules)
- JavaScript and Groovy syntax validation
- Camunda API usage verification (
execution.getVariable(), etc.) - Variable naming conventions
- Null/undefined checks
- JSON operation safety
- Java interoperability validation
- Code smell detection (magic numbers, long functions, deep nesting)
- Error handling patterns
4. Security Scanning (5 rules)
- Hardcoded credentials detection (passwords, API keys, tokens)
- SQL injection risk patterns
- Expression injection vulnerabilities
- Sensitive data in variable names
- Authorization token exposure
5. Performance & Quality (10 rules)
- Synchronous blocking code detection (infinite loops, Thread.sleep)
- Async continuation warnings
- Job executor retry configuration
- Listener ordering issues
- Unused variable detection
- Compensation handler validation
- Reserved variable name conflicts
How It Works¶
Validation Process¶
- Model Parsing - Loads BPMN/DMN XML using moddle parsers with Camunda extensions
- Rule Execution - Each enabled rule analyzes the model structure and content
- Issue Collection - Problems are categorized as errors (must fix) or warnings (should fix)
- Result Presentation - Issues displayed with severity, rule name, message, and element ID
- Filtering & Export - Results can be filtered and exported for team review
Rule Severity Levels¶
Error (Red)
- Model cannot be deployed or will fail at runtime
- Must be fixed before deployment
- Examples: Missing service task implementation, invalid expression syntax, missing timer definition
Warning (Yellow)
- Model will deploy but violates best practices
- Should be fixed to improve maintainability, performance, or security
- Examples: Missing documentation, hardcoded credentials, unused variables
Using the Model Validator¶
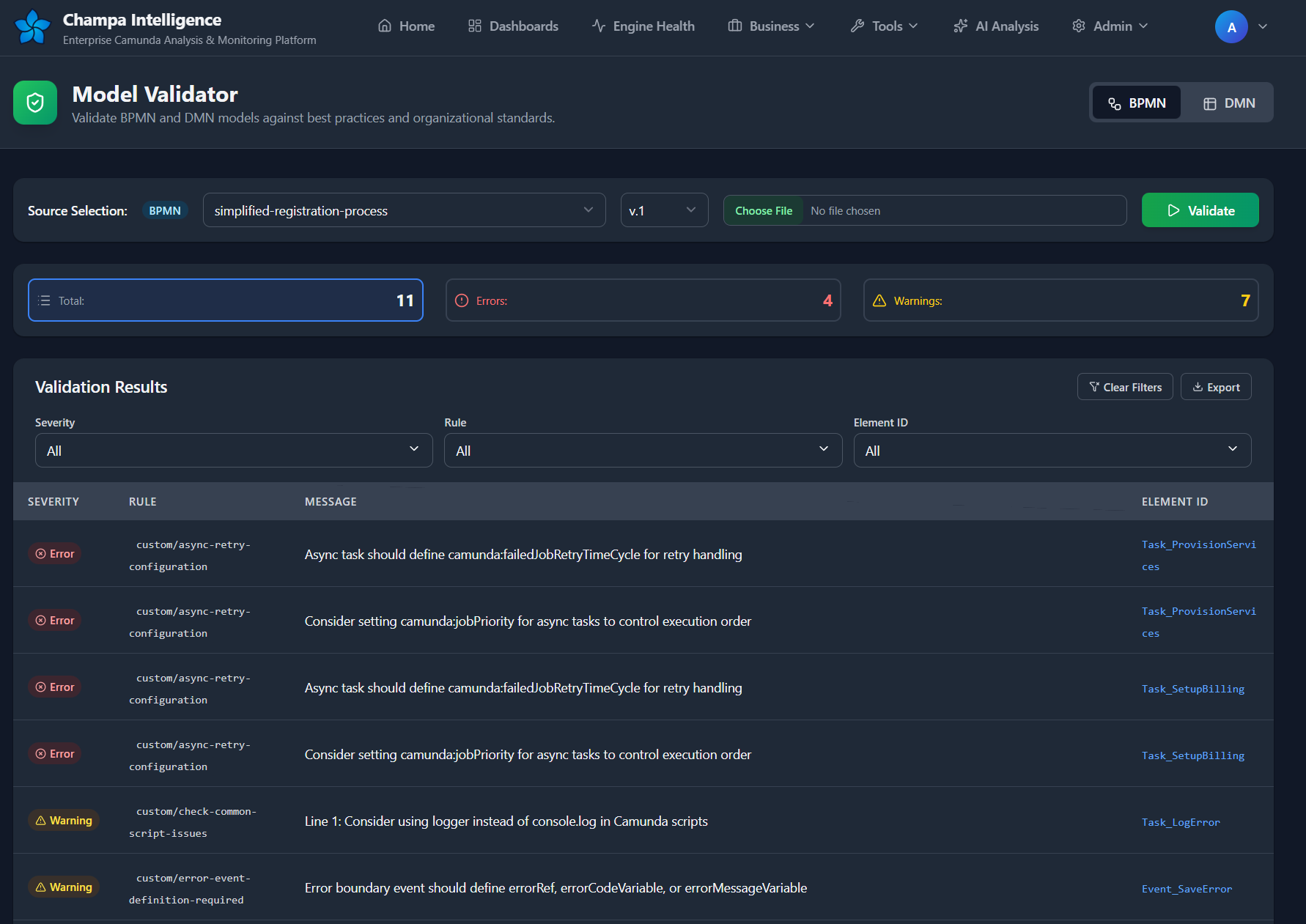
Validating from Database¶
Step 1: Select Model Type Choose between BPMN or DMN using the toggle at the top right.
Step 2: Select Model - For BPMN: Choose a process from the dropdown - For DMN: Choose a decision definition from the dropdown
Step 3: Select Version Choose which version to validate (automatically loads latest by default).
Step 4: Run Validation Click the "Validate" button. Results appear within seconds.
Validating from File¶
Step 1: Upload File Click the file upload input and select a .bpmn, .dmn, or .xml file.
Step 2: Auto-Detection The system automatically detects whether the file is BPMN or DMN based on XML namespaces.
Step 3: Run Validation Click "Validate" to analyze the uploaded file.
Understanding Results¶
Summary Cards Three color-coded cards show:
- Total Issues - All problems detected
- Errors - Critical issues (red)
- Warnings - Best practice violations (yellow)
Click any card to filter results by severity.
Results Table Each row shows:
- Severity - Error or Warning with icon
- Rule - Which validation rule triggered
- Message - Description of the issue
- Element ID - BPMN/DMN element that has the problem
Filtering Results¶
Severity Filter
- Show only errors
- Show only warnings
- Show all (default)
Rule Filter
- Filter by specific rule names
- Searchable dropdown for quick finding
- Multi-select to show multiple rules
Element ID Filter
- Filter to specific BPMN/DMN elements
- Useful when fixing issues in a particular subprocess or decision
Clear Filters Button
Reset all filters to show complete results.
Exporting Results¶
Click the "Export" button to download results as CSV with columns:
- Severity
- Rule
- Message
- Element ID
Share with your team, attach to pull requests, or track fixes in your issue tracker.
Rule Categories Explained¶
Best Practice Rules¶
executable-process-required (Error)
Fix: In Camunda Modeler, check "Executable" in process properties.element-name-required (Warning)
Fix: Add descriptive names to all tasks, events, and gateways.gateway-outgoing-flows-named (Warning)
Fix: Label all outgoing flows from gateways (e.g., "yes", "no", "approved").process-documentation-required (Warning)
Fix: Add documentation in the process properties panel.Camunda-Specific Rules¶
service-task-implementation-required (Error)
Fix: Configure how the service task executes (Java class, delegate expression, or external task topic).user-task-assignee-or-candidate (Error)
Fix: Specify who should work on the task.timer-definition-required (Error)
Fix: Add timer configuration (e.g.,PT5M for 5 minutes). external-task-topic-required (Error)
Fix: Set the topic name for external task workers.multi-instance-configuration (Error)
Fix: Configure collection to iterate over and variable name for each element.Script Validation Rules¶
script-format-required (Error)
Fix: Set script format tojavascript, groovy, etc. validate-javascript-syntax (Error)
Fix: Correct JavaScript syntax errors.validate-camunda-api-usage (Warning)
Fix: Use correct method nameexecution.getVariable(). validate-variable-naming (Warning)
Fix: Rename touserData. check-common-script-issues (Warning)
Fix: Addvar result = ... or const result = .... detect-code-smells (Warning)
Fix: Replace withconst ONE_DAY_MS = 86400000;. validate-null-undefined-checks (Warning)
Fix: Add null check before accessing properties:const customer = execution.getVariable('customer');
if (customer && customer.email) {
// safe to use customer.email
}
Security Rules¶
security-hardcoded-secrets (Error)
Fix: Move credentials to process variables or external configuration.// Bad
const password = "mySecretPass123";
// Good
const password = execution.getVariable('apiPassword');
sql-injection-detection (Error)
Fix: Use parameterized queries or properly escape inputs.// Bad
const sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = " + userId;
// Good
const sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?";
// Use prepared statements in your Java delegate
expression-injection-risk (Error)
Fix: Validate/sanitize user input before using in expressions.Performance Rules¶
detect-synchronous-blocking-code (Warning)
Fix: Replace with timer boundary event or intermediate timer event.async-retry-configuration (Warning)
Fix: Set retry configuration likeR3/PT5M (3 retries, 5-minute intervals). listener-ordering-issues (Warning)
Fix: Reduce number of listeners or document execution order clearly.Configuration & Customization¶
Rule Configuration Files¶
Rules are defined in JSON configuration files:
BPMN Rules: rules.bpmnlintrc
{
"extends": "bpmnlint:recommended",
"rules": {
"label-required": "warn",
"custom/script-format-required": "error",
"custom/security-hardcoded-secrets": "error"
}
}
DMN Rules: rules.dmnlintrc
{
"rules": {
"dmn/dmn-decision-id-required": "error",
"dmn/camunda-history-time-to-live-recommended": "warn"
}
}
Customizing Rules¶
Rule Severity Levels:
"error"- Must be fixed (red)"warn"- Should be fixed (yellow)"off"- Rule disabled
Admin Configuration¶
Administrators can customize rules via the Linter Admin interface:
- Enable/disable rules
- Change severity levels
- Configure rule-specific options
- Save as organizational standards
Rules are stored in the database and applied automatically to all validations.
Integration with Development Workflow¶
Pre-Deployment Validation¶
Before Every Deployment:
- Export BPMN/DMN from Camunda Modeler
- Upload to Model Validator
- Fix all errors (red)
- Address warnings (yellow) where practical
- Deploy to Camunda engine
Code Review Process¶
Pull Request Checklist:
- [ ] Model uploaded to validator
- [ ] Zero errors reported
- [ ] Security warnings reviewed and addressed
- [ ] Performance warnings considered
- [ ] Validation results attached to PR
Best Practices¶
Model Development¶
1. Validate Early and Often
- Validate after major changes
- Don't wait until model is "complete"
- Easier to fix issues incrementally
2. Start with Errors
- Always fix red (error) issues first
- Many warnings become obvious after errors are fixed
- Prioritize deployment-blocking issues
3. Address Security Warnings
- Never ignore security-related warnings
- Review all script content for sensitive data
- Use variables for credentials, not hardcoded values
4. Document as You Go
- Add element names and documentation during modeling
- Don't leave as "Task_1", "ServiceTask_5"
- Future you (and your team) will thank you
Team Standards¶
1. Define Your Rule Set
- Agree on which warnings are mandatory
- Document exceptions and why they're acceptable
- Review and update rules quarterly
2. Share Results
- Export and attach to PRs/tickets
- Discuss patterns in team meetings
- Learn from common mistakes
3. Training
- Show new team members the validator early
- Explain why each rule exists
- Review actual caught issues as examples
Performance Tips¶
For Large Models:
- Break complex processes into call activities
- Validate subprocesses independently
- Address high-impact warnings first
Script Optimization:
- Keep scripts under 50 lines
- Extract complex logic to Java delegates
- Use built-in Camunda features over custom code
Troubleshooting¶
Model Won't Load¶
Issue: "Failed to parse BPMN/DMN"
Solutions:
- Verify file is valid XML
- Check file is actually BPMN/DMN (not corrupted)
- Ensure file contains proper namespaces
- Try re-exporting from Camunda Modeler
False Positives¶
Issue: Rule reports problem that isn't actually an issue
Solutions:
- Check if rule has configurable options
- Document why it's a false positive in model documentation
- Consider disabling rule if frequently problematic
- Report to admin for rule refinement
Performance Issues¶
Issue: Validation takes too long
Solutions:
- Validate smaller sections of process
- Disable optional warnings temporarily
- Check for extremely large scripts or expressions
- Consider model refactoring if too complex
Examples¶
Example 1: Fixing Service Task¶
Before Validation:
<serviceTask id="Task_SendEmail" name="Send Email">
<!-- No implementation defined -->
</serviceTask>
Validation Results:
After Fix:
<serviceTask id="Task_SendEmail" name="Send Email"
camunda:type="external"
camunda:topic="email-sender">
</serviceTask>
Example 2: Fixing Script Issues¶
Before Validation:
// Script in Script Task
customer = execution.getVariable("customer");
email = customer.email;
execution.setVariable("recipientEmail", email);
Validation Results:
⚠️ Warning: Variable "customer" assigned without declaration
⚠️ Warning: Property access on "customer" without null check
After Fix:
const customer = execution.getVariable("customer");
if (customer && customer.email) {
execution.setVariable("recipientEmail", customer.email);
} else {
throw new Error("Customer or email not found");
}
Example 3: Fixing Security Issue¶
Before Validation:
Validation Results:
After Fix:
const apiKey = execution.getVariable("apiKey");
const url = execution.getVariable("apiEndpoint");
if (!apiKey) {
throw new Error("API key not configured");
}
FAQ¶
Q: Can I validate models before they're deployed?
A: Yes! That's the primary use case. Upload BPMN/DMN files from Camunda Modeler before deploying to catch issues early.
Q: Will fixing warnings break my process?
A: No. Warnings indicate best practice violations but won't prevent deployment. However, fixing them improves maintainability and prevents future issues.
Q: Can I disable specific rules?
A: Yes. Administrators can customize rules via Linter Admin interface. Rules can be turned off, downgraded to warnings, or configured.
Q: Why are some rules marked "custom"?
A: "custom/" prefix indicates Camunda-specific or organization-specific rules beyond the standard BPMN linter rules.
Q: How do I add new rules?
A: Currently requires code changes. Contact your Champa Intelligence administrator or submit a feature request for new rule types.
Q: Can I validate during modeling in Camunda Modeler?
A: Not directly. You must export and upload to Champa Intelligence. However, Camunda Modeler has its own basic linting that catches some issues.
Q: What happens if I deploy a model with errors?
A: Errors indicate likely runtime failures. The model may deploy but fail when executed. Always fix errors before deployment.
Q: How do I know which line of script has an issue?
A: Script validation messages include line numbers (e.g., "Line 5: Variable not declared"). Reference these when fixing scripts.
Q: Can I validate multiple models at once?
A: Currently, validation is one model at a time. Upload and validate each BPMN/DMN file separately.
Q: Does validation work on older Camunda versions?
A: Yes. The validator works with any valid BPMN 2.0 or DMN 1.3 XML, regardless of Camunda version. However, some Camunda-specific rules assume Camunda 7 conventions.
Summary¶
The Model Validator transforms process quality assurance from manual review to automated enforcement:
✅ 70+ rules catch errors, enforce standards, and identify security risks
✅ Real-time validation provides instant feedback during development
✅ Customizable rules adapt to your organization's standards
✅ Export results for team collaboration and CI/CD integration
✅ Dual support for both BPMN and DMN models
By integrating validation into your development workflow, teams deploy higher-quality processes with fewer runtime surprises.